Sqoop vs. Flume Battle of the Hadoop ETL tools
ProjectPro
JUNE 6, 2025
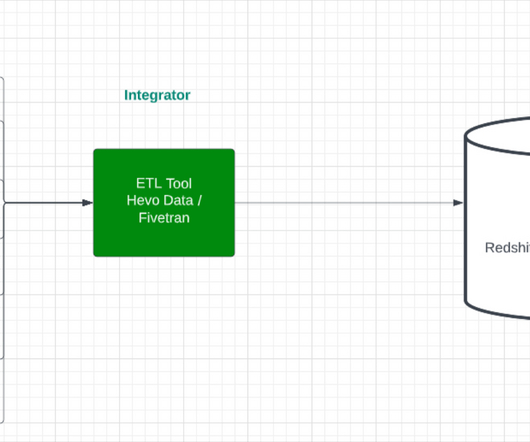
Hadoop Sqoop and Hadoop Flume are the two tools in Hadoop which is used to gather data from different sources and load them into HDFS. Sqoop in Hadoop is mostly used to extract structured data from databases like Teradata, Oracle, etc., Need for Apache Sqoop How Apache Sqoop works? Need for Flume How Apache Flume works?


















Let's personalize your content