Data Pipeline- Definition, Architecture, Examples, and Use Cases
ProjectPro
DECEMBER 7, 2021
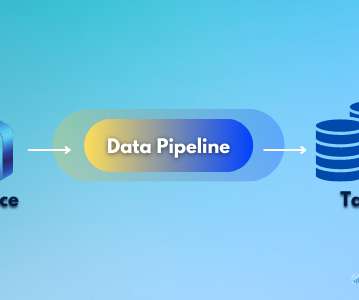
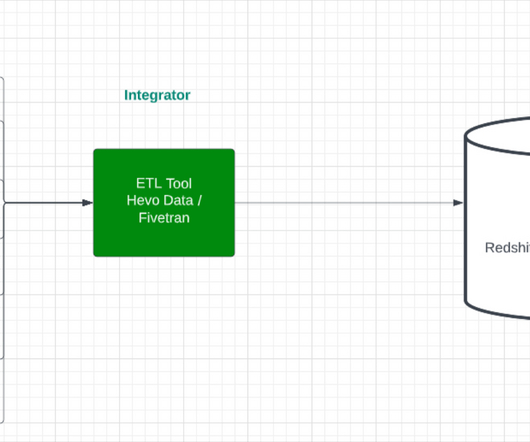
To understand the working of a data pipeline, one can consider a pipe that receives input from a source that is carried to give output at the destination. And based on the business use cases, what happens inside the pipeline is decided. A pipeline may include filtering, normalizing, and data consolidation to provide desired data.








Let's personalize your content